How to collect the first round of environmental tax payment? To whom?
TIME:
2018-04-24 14:26
On April 1st, the environmental protection tax entered its first taxation period. This is the first tax in Chinese history aimed at environmental protection and implemented quarterly declaration. According to data released by the State Administration of Taxation on February 27th, tax authorities across the country have identified and recognized over 260000 environmental protection tax taxpayers.
On January 1, 2018, the Environmental Protection Tax Law of the People's Republic of China and the Implementation Regulations of the Environmental Protection Tax Law of the People's Republic of China were officially implemented, and the Regulations on the Administration of the Collection and Use of Pollutant Discharge Fees were simultaneously abolished. The arrival of new taxes has made the "pollution fee" that has existed for over a decade a thing of history. Experts and scholars have evaluated that the Environmental Protection Tax Law is the first law in China to reflect the "green tax system", ending the nearly 40 year old pollution fee system and an important milestone in China's "fee to tax" process.
Who is the taxpayer of environmental protection tax? How will it be charged? How do taxes belong? Below is an answer for everyone.
Who is the taxpayer?
Article 2 of the Environmental Protection Tax Law stipulates that enterprises, institutions, and other producers and operators that directly discharge taxable pollutants into the environment within the territory of the People's Republic of China and other sea areas under its jurisdiction shall be taxpayers of environmental protection tax and shall pay environmental protection tax in accordance with the provisions of this Law.
Based on this, we can see the following points:
(1) Environmental protection tax applies not only to land areas but also to sea areas.
(2) Environmental protection tax is only levied on those who directly discharge taxable pollutants into the environment.
(3) Environmental protection tax is only levied on taxable pollutants, and environmental protection tax is not levied on pollutants discharged other than taxable pollutants.
(4) Enterprises, institutions, and other producers and operators are taxpayers, and general natural persons do not belong to the category of environmental protection tax taxpayers.
What are the situations where taxes are not paid?
For those who indirectly discharge taxable pollutants into the environment or whose taxable pollutants have not been discharged externally, no environmental protection tax shall be paid for the corresponding pollutants. The situations where the corresponding pollutant environmental protection tax is not paid as specified in Article 4 of the Environmental Protection Tax Law include:
(1) Enterprises, institutions, and other producers and operators discharge taxable pollutants into legally established centralized sewage treatment and domestic waste treatment facilities;
(2) Enterprises, institutions, and other producers and operators store or dispose of solid waste in facilities and places that meet national and local environmental protection standards.
Article 4 of the Implementation Regulations of the Environmental Protection Tax Law stipulates that "comprehensive utilization and harmless treatment of livestock and poultry breeding waste in accordance with the law does not constitute direct discharge of pollutants into the environment, and no environmental protection tax shall be paid
What are the taxable pollutants?
Atmosphere, water, solids, and noise are the main pollutants that affect the environment, and internationally, taxes are generally chosen for these four types of pollutants. The objects of collection under China's environmental protection tax law are also these four types of pollutants.
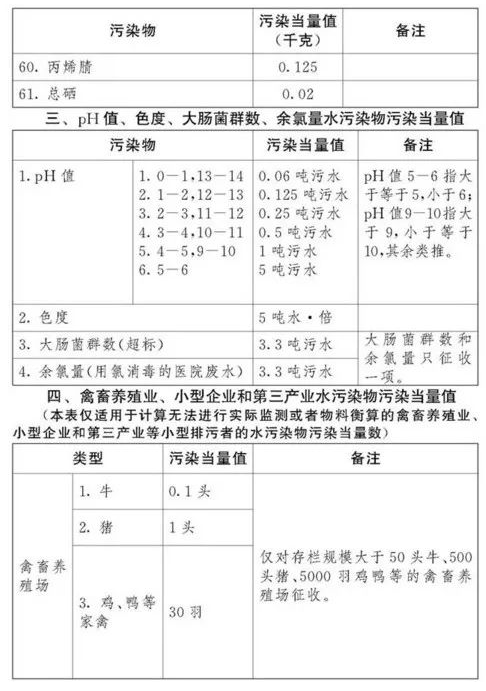
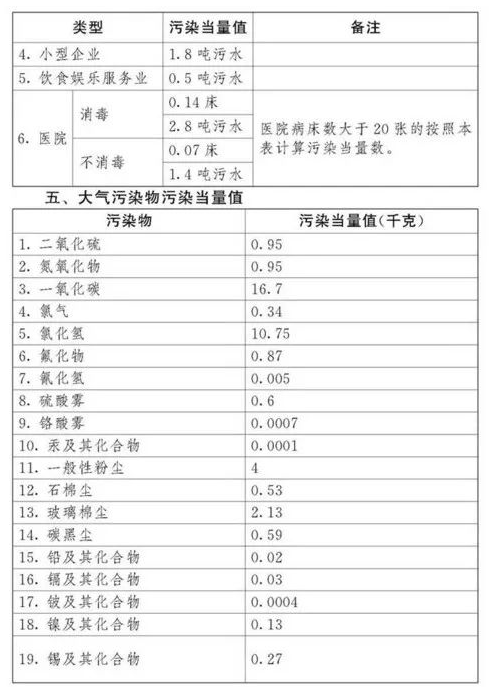
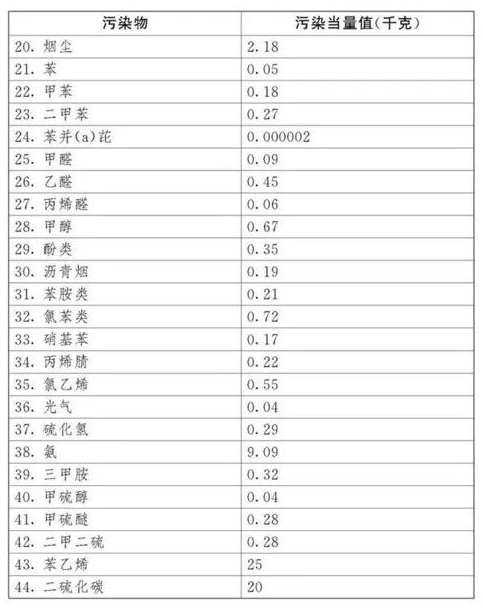
Environmental Protection Tax Law Regulations,Taxable pollutants refer to atmospheric pollutants, water pollutants, solid waste, and noise specified in the "Table of Tax Items and Amounts of Environmental Protection Tax" and "Table of Taxable Pollutants and Equivalent Values" attached to the Environmental Protection Tax Law. In terms of sea areas, taxable pollutants include atmospheric pollutants, water pollutants, and solid waste.
It should be noted that,Solid waste is not limited to solid waste, but also includes semi solid and liquid waste. Article 88 of the Law on the Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Waste stipulates that "Solid waste refers to solid, semi-solid, and gaseous objects and substances that have lost their original utilization value or have been abandoned or abandoned in production, daily life, and other activities, as well as those that are included in solid waste management according to laws and administrative regulations, Article 89 stipulates that "the prevention and control of pollution by liquid waste shall be governed by this Law".
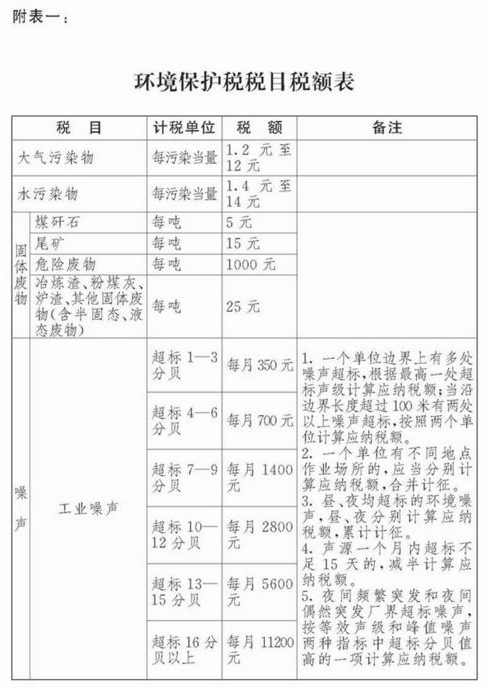
Tax amount of environmental protection tax
The amount of environmental protection tax shall be implemented in accordance with the "Table of Environmental Protection Tax Items and Amounts" attached to the Environmental Protection Tax Law. The tax amount for solid waste and noise is fixed, as detailed in Appendix 1; The determination and adjustment of the specific applicable tax amount for taxable air pollutants and water pollutants shall be proposed by the provincial-level people's government within the tax and fee range of 1.2 to 12 yuan per pollution equivalent of air pollutants and 1.4 to 14 yuan per pollution equivalent of water pollutants. The plan shall be submitted to the Standing Committee of the People's Congress at the same level for decision, and shall be filed with the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress and the State Council. The current applicable tax amounts for each province, city, and autonomous region are shown in Appendix 2.
The specific applicable tax amount for marine engineering environmental protection tax shall be implemented according to the tax amount standards applicable to the location of the offshore oil tax (collection) management branch responsible for collecting environmental protection tax. Domestic waste shall be subject to the tax standard for "other solid waste" under the Environmental Protection Tax Law.
Tax basis for four types of pollutants
Environmental protection tax is mainly levied based on the amount of pollutant emissions, but the measurement of pollutant emissions is relatively complex, with different measurement standards for air, water, solid waste, noise, etc.
Article 7 of the Environmental Protection Tax Law stipulates that the tax basis for taxable pollutants shall be determined according to the following methods:
(1) Taxable atmospheric pollutants are determined based on the pollution equivalent converted from pollutant emissions;
(2) Taxable water pollutants are determined based on the pollution equivalent converted from pollutant emissions;
(3) Taxable solid waste is determined based on the amount of solid waste discharged;
(4) Taxable noise is determined by decibels exceeding national standards.
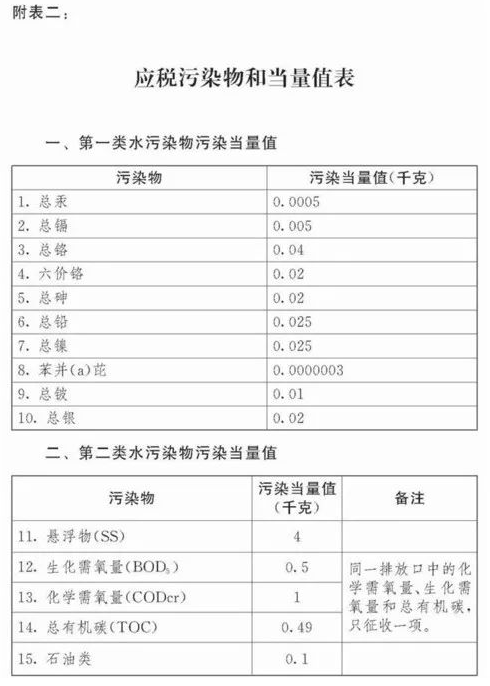
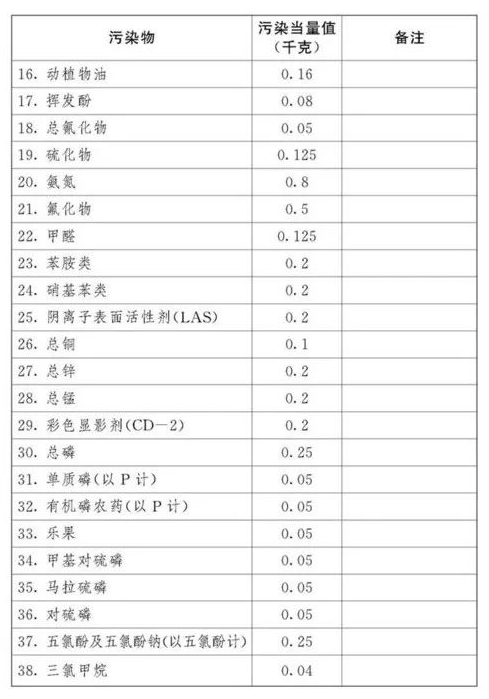
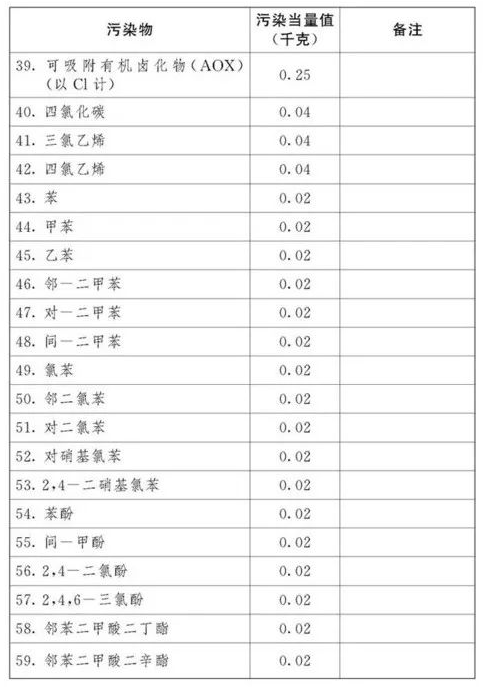
The pollution equivalent number of taxable air pollutants and water pollutants is calculated by dividing the emission amount of the pollutant by the pollution equivalent value of the pollutant. The specific pollution equivalent values of each taxable air pollutant and water pollutant shall be executed in accordance with the "Taxable Pollutants and Equivalent Values Table" attached to this Law.
How to calculate the emission value of taxable pollutants?
According to Article 10 of the Environmental Protection Tax Law, the emissions of taxable atmospheric pollutants, water pollutants, solid waste, and the decibels of noise shall be calculated in the following methods and order:
(1) Taxpayers who install and use automatic monitoring equipment for pollutants that comply with national regulations and monitoring standards shall be calculated based on the automatic monitoring data of pollutants;
(2) Taxpayers who have not installed and used automatic monitoring equipment for pollutants shall be calculated based on monitoring data issued by monitoring institutions that comply with relevant national regulations and monitoring standards;
(3) If the monitoring conditions are not met due to various types of pollutants emitted, the calculation shall be based on the pollution discharge coefficient and material balance method specified by the competent environmental protection department of the State Council;
(4) If the calculation cannot be carried out according to the methods specified in items 1 to 3 of this article, the calculation shall be verified and approved according to the sampling calculation method specified by the environmental protection department of the people's government of the province, autonomous region, or municipality directly under the central government.
According to the Implementation Regulations of the Environmental Protection Tax Law, taxpayers under the second provision shall be deemed to have obtained monitoring data from their own monitoring of pollutants that comply with relevant national regulations and monitoring standards.
How to calculate the emission value when taxpayers violate the law?According to Article 7 of the Implementation Regulations of the Environmental Protection Tax Law, if a taxpayer falls under any of the following circumstances, the amount of taxable air and water pollutants generated in the current period shall be used as the discharge amount of pollutants:
(1) Failure to install and use automatic monitoring equipment for pollutants in accordance with the law, or failure to network automatic monitoring equipment for pollutants with monitoring equipment of environmental protection authorities;
(2) Damage or unauthorized movement or alteration of automatic monitoring equipment for pollutants;
(3) Tampering or falsifying pollutant monitoring data;
(4) Illegally discharge taxable pollutants through concealed pipes, seepage wells, seepage pits, injection or dilution emissions, and abnormal operation of pollution prevention and control facilities;
(5) Making false tax declarations.
What situations are temporarily exempt from tax?
The Environmental Protection Tax Law stipulates 5 temporary tax exemptions. Article 12 of the Environmental Protection Tax Law stipulates that the following situations shall be temporarily exempted from environmental protection tax:
(1) Emissions of taxable pollutants from agricultural production (excluding large-scale aquaculture);
(2) Emissions of taxable pollutants from mobile pollution sources such as motor vehicles, railway locomotives, non road mobile machinery, ships, and aircraft;
(3) The discharge of corresponding taxable pollutants from urban and rural sewage centralized treatment and domestic waste centralized treatment facilities established in accordance with the law shall not exceed the discharge standards set by the state and local authorities;
(4) Solid waste comprehensively utilized by taxpayers that meets national and local environmental protection standards;
(5) Other situations approved by the State Council for tax exemption.
The tax exemption provisions of the fifth item of the preceding paragraph shall be reported by the State Council to the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress for the record.
Tax reduction includes the following two situations.Article 13 of the Environmental Protection Tax Law stipulates that if the concentration of taxable atmospheric or water pollutants discharged by taxpayers is lower than 30% of the national and local pollutant discharge standards, the environmental protection tax shall be levied at a reduced rate of 75%. If the concentration of taxable atmospheric or water pollutants emitted by taxpayers is lower than 50% of the national and local pollutant discharge standards, an environmental protection tax of 50% shall be levied.